 While I have written extensively about arthritis in this blog, this is my first post on Bursitis. Similar to arthritis, bursitis is largely about inflammation. While arthritis is inflammation in the joint, bursitis is inflammation in the bursa capsule, which for the most part, is located near joints.
While I have written extensively about arthritis in this blog, this is my first post on Bursitis. Similar to arthritis, bursitis is largely about inflammation. While arthritis is inflammation in the joint, bursitis is inflammation in the bursa capsule, which for the most part, is located near joints.
What is Bursitis?
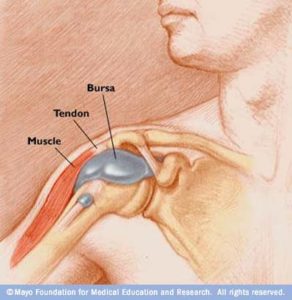
Simply stated, Bursitis is a sickness of the bursa.
Bursas are thick, liquid-filled sacs that provide lubrication and cushioning between bones and other material like muscles and tendons.
As bursa sacs are located near the joints, bursitis symptoms are first experienced as pain at the joints, accompanied by a decreased range of motion. There are over 150 bursas in the body, with most located near bony prominences, such as the elbows, knees, shoulders and hips. The ankles and feet are also common places for bursitis to develop. The nature of the bursa is to swell with an acute insult and to resolve slowly and often, incompletely.
What Causes Bursitis?
Like arthritis, bursitis can be caused by over-use, impact, lack of circulation, improper alignment and repetitive motion. Generally, arthritis and bursitis go hand in hand – if you have one, you often have the other. Tennis elbow, for example, is a combination of bursitis and arthritis at the elbow joint.
In general, it can be hard to differentiate between arthritis and bursitis as swelling in one part of the anatomy drastically affects the whole environment and leads to more swelling.
Bursitis:
- Swelling in the bursa sac
- Decrease in circulation
- Calcium build-up
- Fluid build-up
- On the bone near the joint
Arthritis:
- Swelling in the joint capsule
- Decrease in circulation
- Calcium build-up
- Inside the joint
How to Treat Bursitis?
The good news. Resolving bursitis is all about resolving inflammation in the bursa sac, and as bursas are often close to the 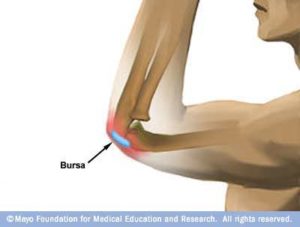 surface of the skin, bursitis can be addressed with massage. We can work directly on the bursa tissue. In the case of arthritis, however, access to the joint capsule is not as straight-forward. Treatment for arthritis is also more dependent on range of motion. While bursitis benefits from range of motion exercises as well, in some cases, resolution occurs primarily through that direct massage.
surface of the skin, bursitis can be addressed with massage. We can work directly on the bursa tissue. In the case of arthritis, however, access to the joint capsule is not as straight-forward. Treatment for arthritis is also more dependent on range of motion. While bursitis benefits from range of motion exercises as well, in some cases, resolution occurs primarily through that direct massage.
The most important factor in treatment for bursitis (and arthritis) is the reduction of the swelling. This can happen by way of a few my favorite things: massage, stretching/movement, and proper alignment.
- Massage helps to increase circulation – We can clear stagnant blood and swelling.
- Stretching/movement enhances range of motion.
- Proper alignment maximizes circulation while preventing further issues.
I find it disappointing that the standard AMA protocol for treating bursitis involves immobilizing the effected joint. In my experience movement is one of the best things you can do to remedy the problem. For one thing, if a joint is immobilized due to bursitis, there is a greater chance that the condition will lead to arthritis, which is more difficult to resolve.
My next post will focus on hip bursitis, so stay tuned. In the meanwhile, if you are experiencing bursitis, arthritis or any unspecified pain in or near a joint, please contact us. With some professional massage, stretching and postural alignment you too can feel better forever.
Disclaimer: This information is not suggested as a replacement for medical care. Please consult your physician to learn if this protocol is right for you.
